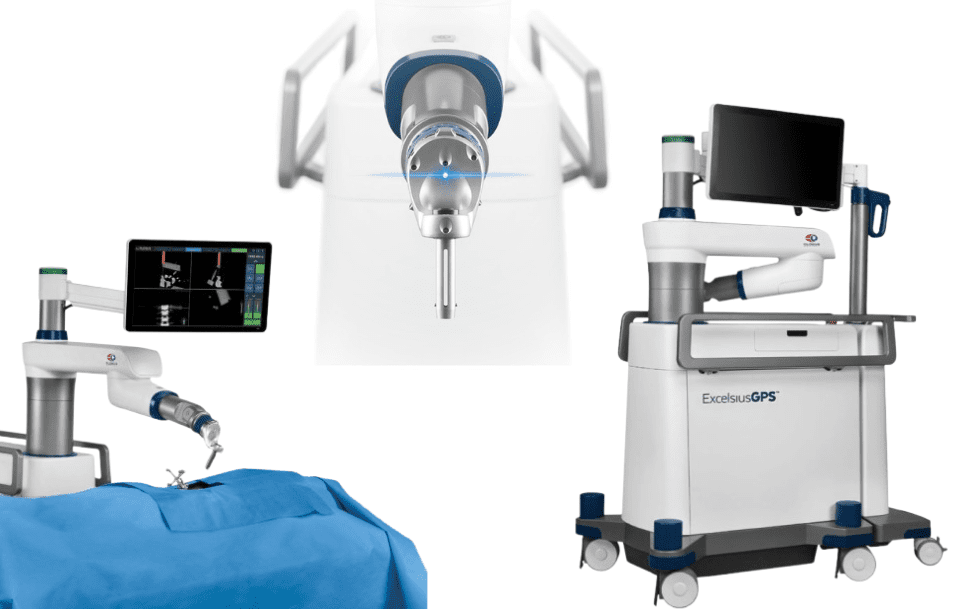
At HKAH, we employ three advanced robotic systems to enhance our surgical capabilities:

ExcelsiusGPS® Robotic Navigation
Common Spine Problems
If there is a problem with the spine, such as intervertebral disc herniation, spinal stenosis, and intervertebral disc degeneration, it can affect various parts of the body. Relevant research shows that up to 80% of adults experience back pain, and spinal disease is one of the common reasons for seeking medical attention. For example, approximately 3 million Americans suffer from a herniated disc each year, while spinal stenosis affects approximately 200,000 Americans. These spinal problems often cause chronic pain, limited mobility, numbness, and weakness, making basic daily activities difficult and affecting the quality of life.
Application of the Robotic Arm Surgical System
Our hospital has introduced Hong Kong's first robotic arm surgical system, ExcelsiusGPS® that can be applied to the entire spine. Robotic arm navigation is mainly used for spinal fixation in spine surgery, such as inserting pedicle screws or fusion devices in the lumbar spine. The system can also be used for cervical spine surgery. Since the bones of the cervical spine are relatively 10 thinner and have lower tolerance for deviation, the assistance of robotic arms can effectively improve the accuracy of surgery.
In robotic arm surgery, doctors can also utilize a computer navigation system to assist in completing the surgery, less use of X-rays will result in lower radiation exposure for both patients and medical staff. Before the surgery, the doctor can pre-plan the positioning of the screws and the ideal screw sizes, which will improve the stability after implantation. Compared with relying solely on X-rays and doctors’ clinical judgment in the past, preoperative planning and accuracy of robotic arm surgeries have been greatly improved.
Advantages of the Entire Spine Robotic Arm Surgical System
- Fast Recovery
- Less Pain
- Less Blood Loss
- Reduced Damage to Surrounding Soft Tissues and Muscles
- Shorter Surgical Duration
- Smaller Incision Size
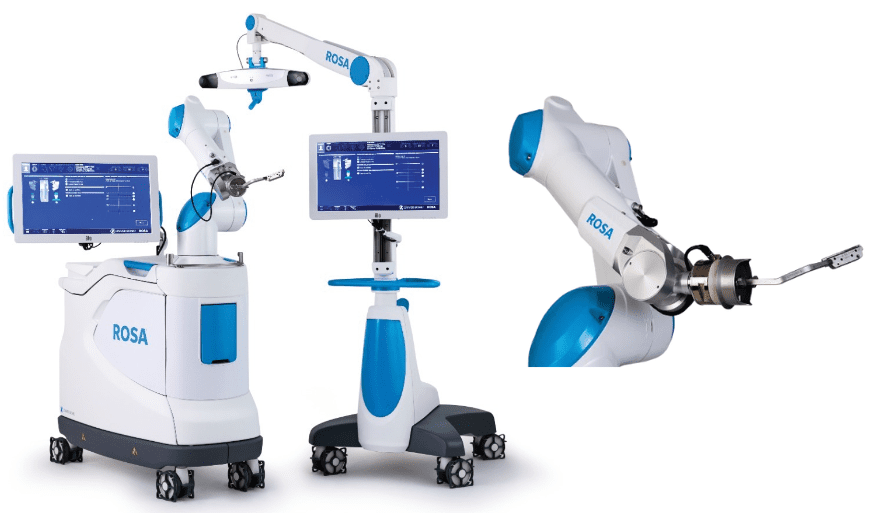
ROSA® Robotic System
Recent Situation
Bone and muscle loss is a common problem in the aging population, and it often leads to knee joint pains. Many patients with this problem have to replace their knee joints by undergoing total knee replacement surgery. Knee replacement surgery is one of the procedures with the longest waiting times in public hospitals. As of June 30, 2024, there were a total of 33,951 cases waiting for this surgery, with an average waiting time of approximately 4 years. Through professional diagnosis by orthopedic surgeon, advanced techniques and materials can be used to replace the joint with an artificial one, relieving the patient's pain and restoring their daily functional ability.
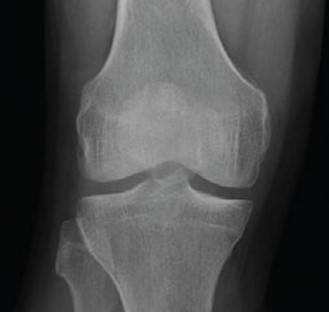
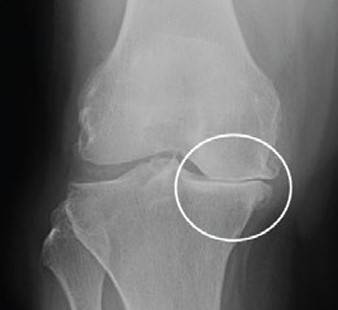
Normal joint space Narrowed joint space
Healthy articular cartilage Worn articular cartilage
Knee Joint Degeneration
Once the knee develops a pathological condition, the joint space narrows, and the articular cartilage is worn down and damaged, leading to pain and even deformity. The common causes include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, and osteonecrosis etc.
If the joint disease becomes severe, and conservative treatment is ineffective, the orthopedist will select the most appropriate knee replacement based on the patient's knee joint condition. The affected bone is removed, and it is replaced with metal. The cartilage portion is substituted with high-molecular- weight polyethylene, eliminating the direct friction of the metal surfaces.
Advantages of Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Replacement
After the professional diagnosis and selection of the appropriate artificial joint for the patient, orthopedic surgeon will perform joint replacement surgery to implant the artificial joint to patient's body. The ROSA® Robotic System provides stable, precise, and highly reproducible cutting, which can help the orthopedic surgeon to perform the surgery more accurately. Moreover, robotic system allows adjustment and personalization of bone cut and artificial joint position, which effectively reduce soft tissue damage and promoting postoperative pain relief, thereby improving surgical outcomes.
- Decreases Postoperative Pain
- Helps in a Faster Return to Daily Life
- Reduces Complications/Blood Loss
- Shortens Hospital Stay

Our hospital has collaborated with Zimmer Biomet to establish the first 'ROSA Robotics Surgery Center of Excellence' in the Greater China region. This center will provide a training base for orthopedic surgeons in Greater China and the Asia-Pacific region, focusing on robotic-assisted joint replacement surgeries. It will facilitate relevant training and academic exchanges, contributing to the popularization and development of robotic joint surgeries.
Da Vinci Xi Robotic Surgical Systems
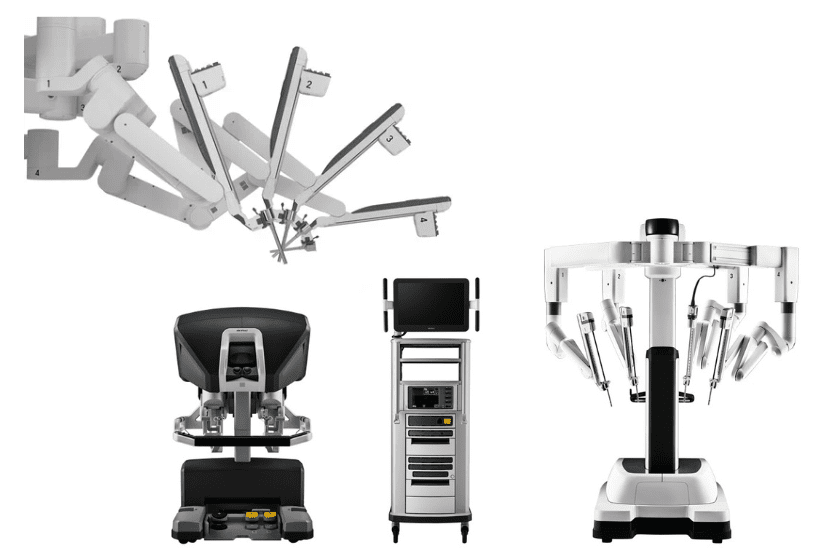
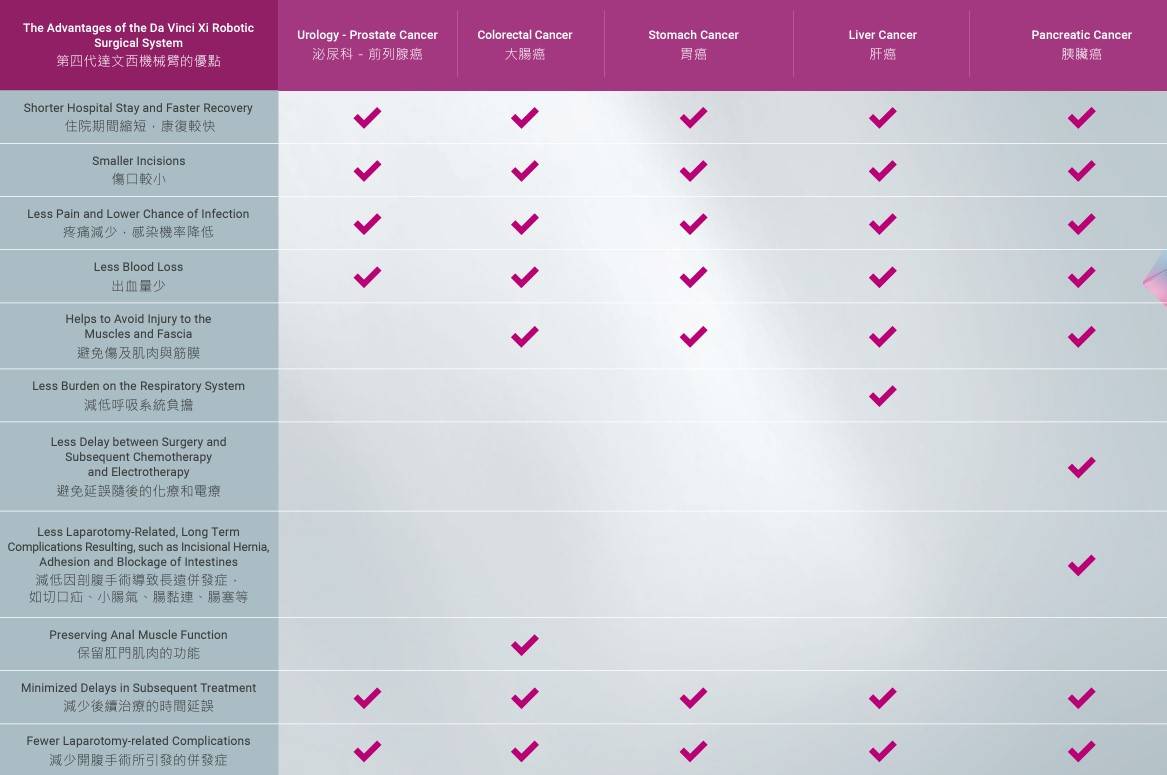
The fourth generation of the Da Vinci Xi Robotic Surgical System is an advanced minimally invasive surgical system, with over 12 million procedures performed worldwide using this technology. The Da Vinci Xi Surgical System is utilized across numerous medical disciplines, particularly in addressing cancers such as stomach cancer, liver cancer, and pancreatic cancer.
Prostate Cancer
Today, robotic prostatectomy is widely used, and in the United States, it has become more common than conventional open surgery. With the assistance of the Da Vinci Surgical System, doctors carefully remove the prostate gland and pelvic lymph nodes using high-definition 3D images while preserving important nerves and blood vessels. This precision enhances patient safety and post-surgery outcomes.
Colorectal Cancer
The robotic surgical system is capable of addressing complicated rectal cancer cases while minimizing side effects, such as impotence, by preserving the pelvic nerve plexus. This system also allows surgeons to operate deeper into the pelvis to effectively remove hard-to-reach tumors while preserving anal muscle function, thus exempting patients from the need for a permanent stoma.
Stomach Cancer
Since the gastric lymph nodes are in close proximity to the aorta, the surgery is generally performed through an open abdominal approach. However, surgeons can also utilize a robotic-assisted system to perform the procedure more efficiently and effectively in removing the potentially infected lymph nodes, while avoiding damage to the nearby major blood vessels.
Liver Cancer
The liver is densely vascularized and closely connected to the bile ducts. The robotic-assisted system can provide a three-dimensional, clear, and magnified real-time image, as well as the ability to filter out any tremor from the surgeon's hands, further improving the precision and safety of the surgical procedure.
Pancreatic Cancer
The robotic-assisted system allows the surgeon to clearly visualize the internal conditions, perform complex procedures within the cavity from different angles, and conveniently dissect tissues in difficult positions or angles, while avoiding damage to nearby major blood vessels. This results in a faster recovery for the patient.


































.jpg)




















