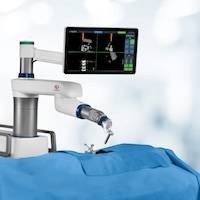
Robot-Assisted Total Knee Replacement Surgery
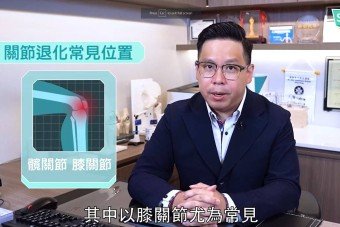
Degenerative knee osteoarthritis is a common joint disease that can lead to cartilage wear, pain, and stiffness in the knee, renders patient difficult to perform daily activities. Traditional knee replacement surgery involves opening the knee joint, removing the damaged cartilage and bone, and replacing the joint with an artificial joint implant to restore the joint function. However, in recent years, robot-assisted total knee replacement surgery has become more widespread. Using computer navigation and robotic arm assistance technology, it precisely performs bone cutting and artificial joint implantation, making it a more accurate, minimally invasive, and efficient knee replacement method.
What is Total Knee Replacement Surgery?
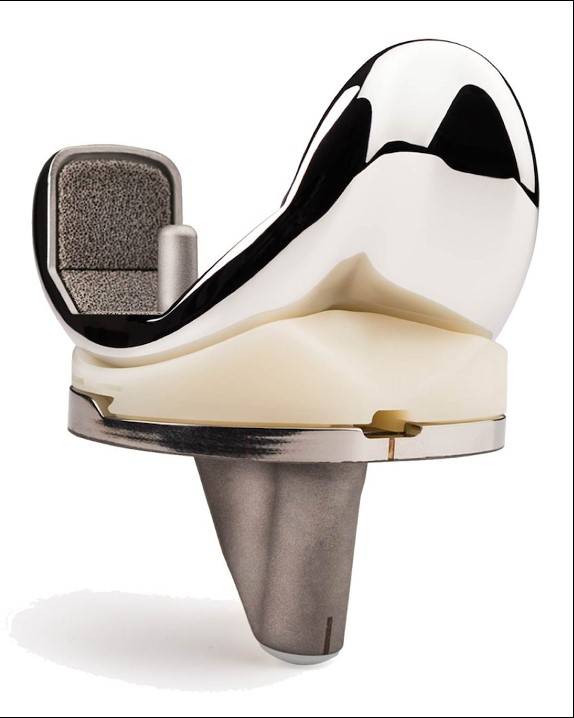
Total knee replacement surgery is an orthopedic procedure that uses an artificial joint to replace a severely worn or damaged knee joint. It is an indicated surgical definitive treatment for various knee pathologies, such as degenerative arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, and osteonecrosis of knee. The principle of total knee replacement surgery is to remove the damaged knee joint cartilage and bone, and then implant an artificial joint. The artificial joint is made of metal alloy and high molecular weight polyethylene, which can mimic the movement and function of native knee joint.
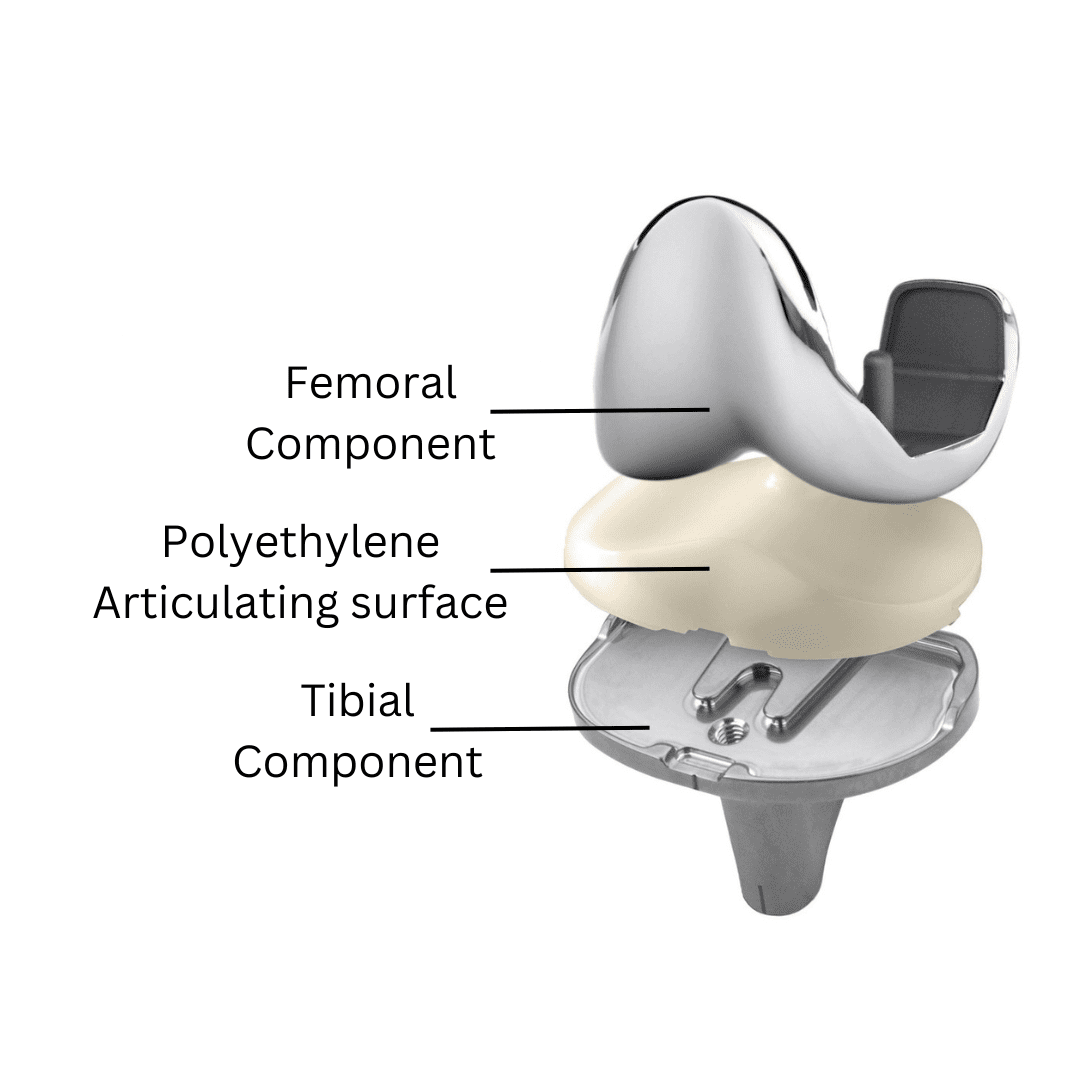
Surgical Characteristics
Preoperative 3D Surgical Planning
Before performing robot-assisted total knee replacement surgery, the patient will undergo imaging examination such as X-Ray, and a virtual three-dimensional bone model will be created on the computer. Doctors can accurately plan the size and position of the artificial joint prosthesis based on the patient's specific anatomy and pathology, and make preparations for the surgery.
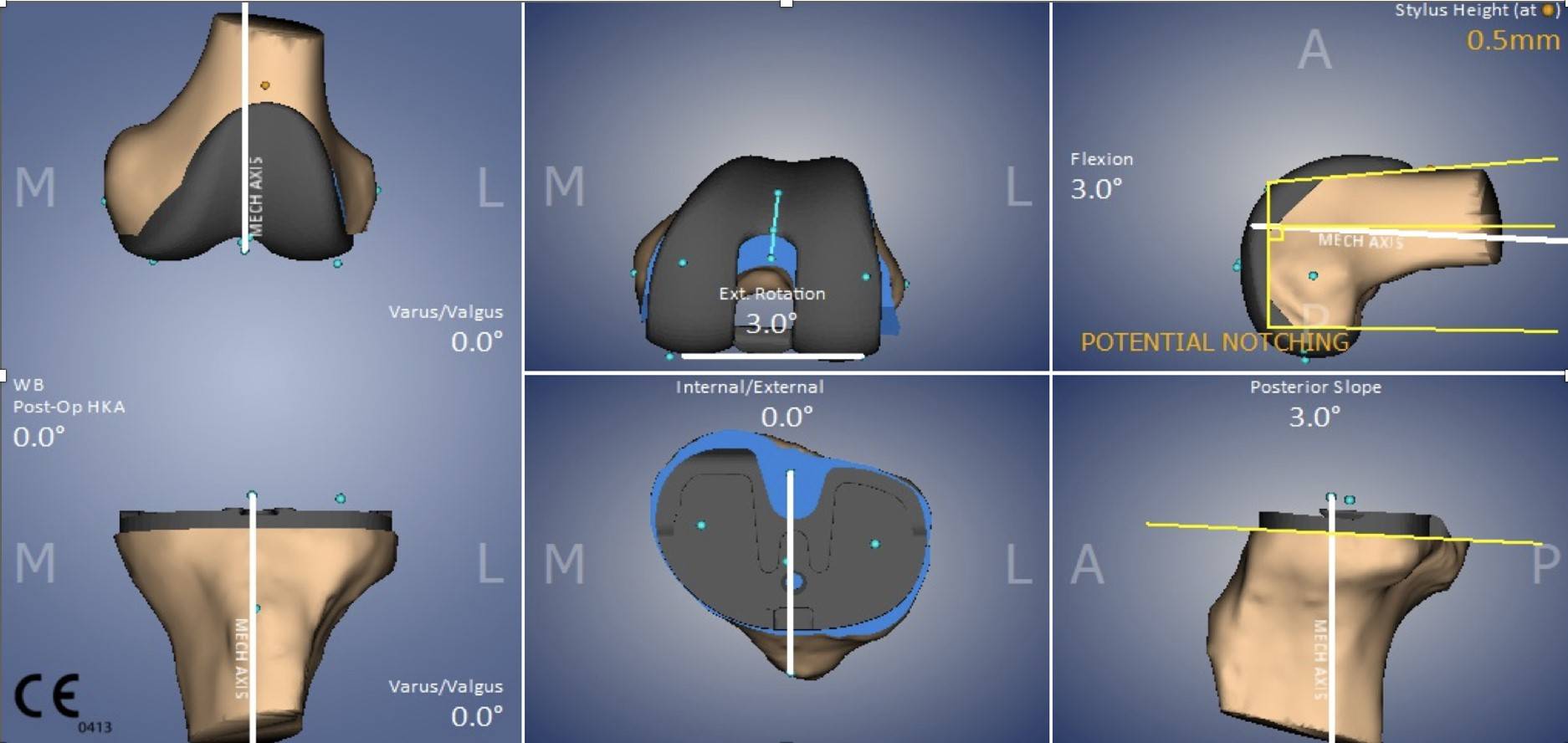
Improved Surgical Accuracy
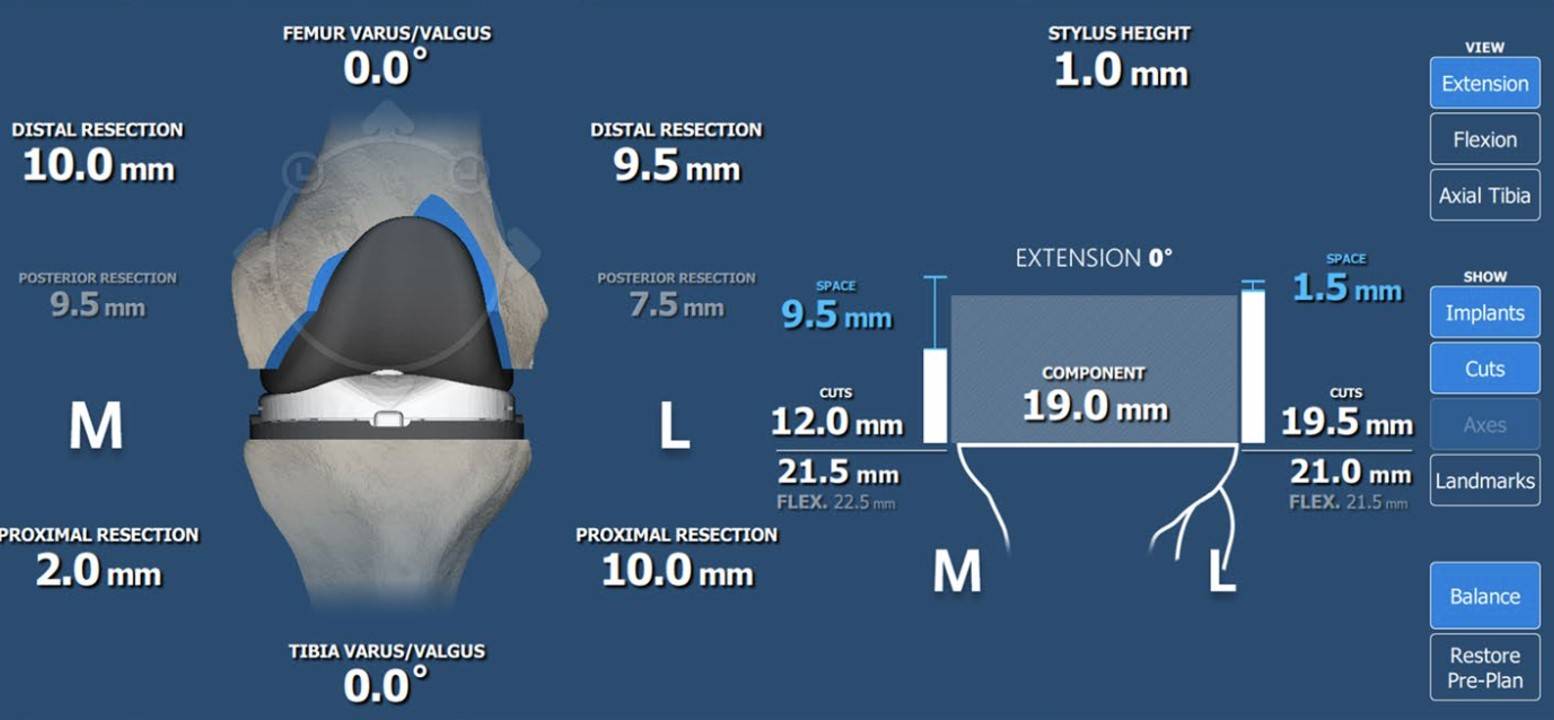
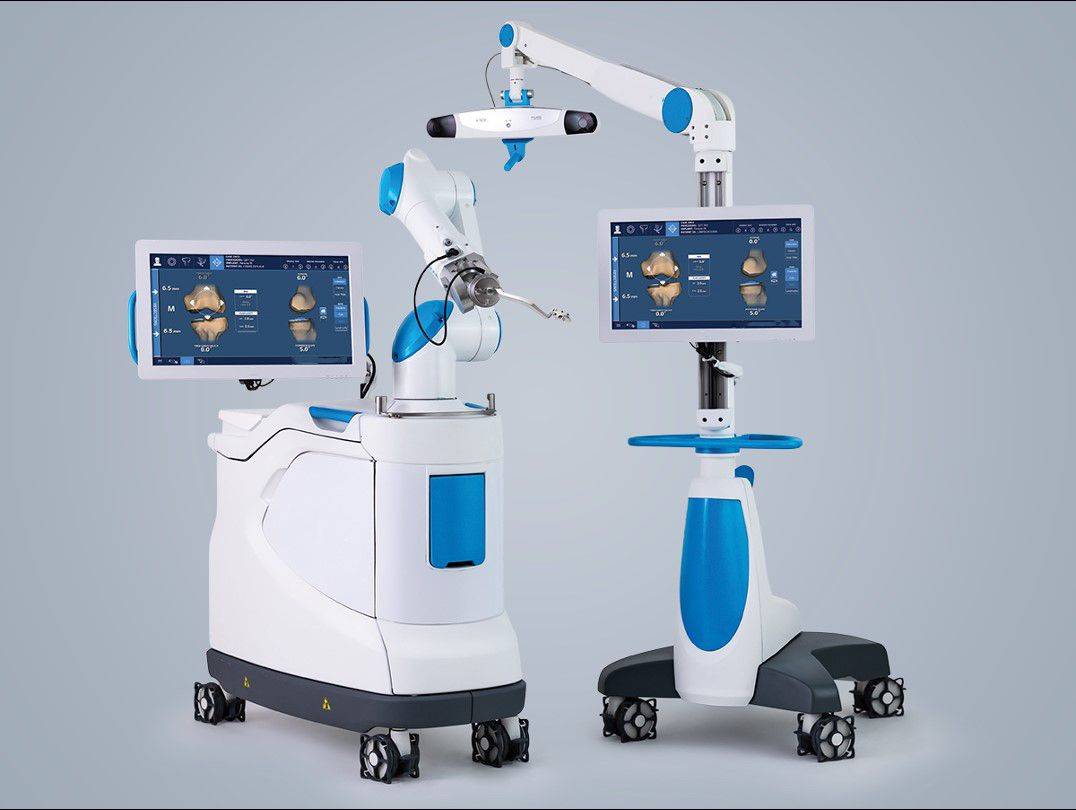
During the surgery, the doctor will use an optical tracking system and a precise robotic arm to assist in bone cutting and implanting the artificial joint, reducing the error to within 1 mm or 1 degree, improving the accuracy and predictability of the surgery, and ensuring a more ideal and accurate placement of the artificial knee joint.
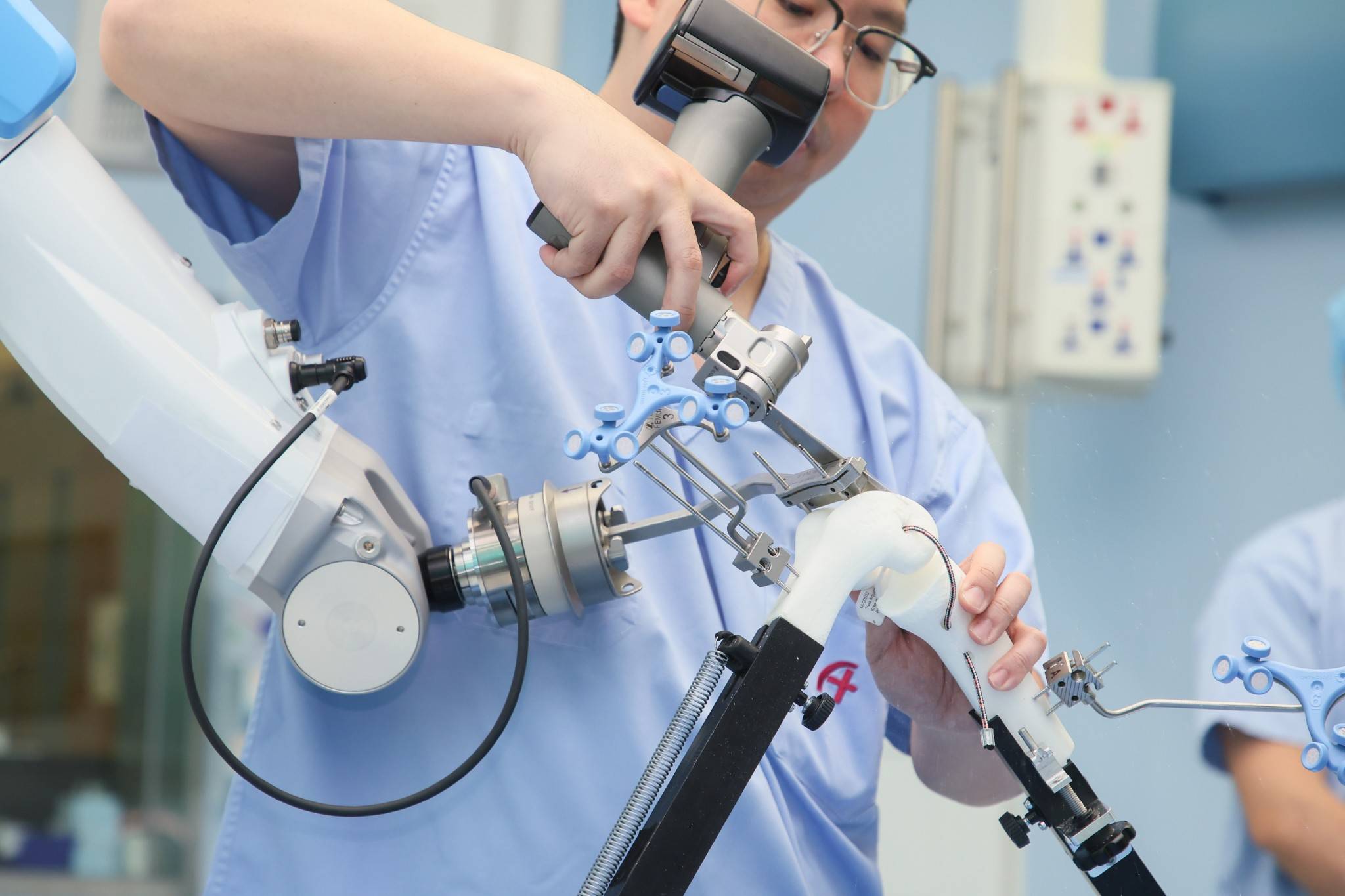
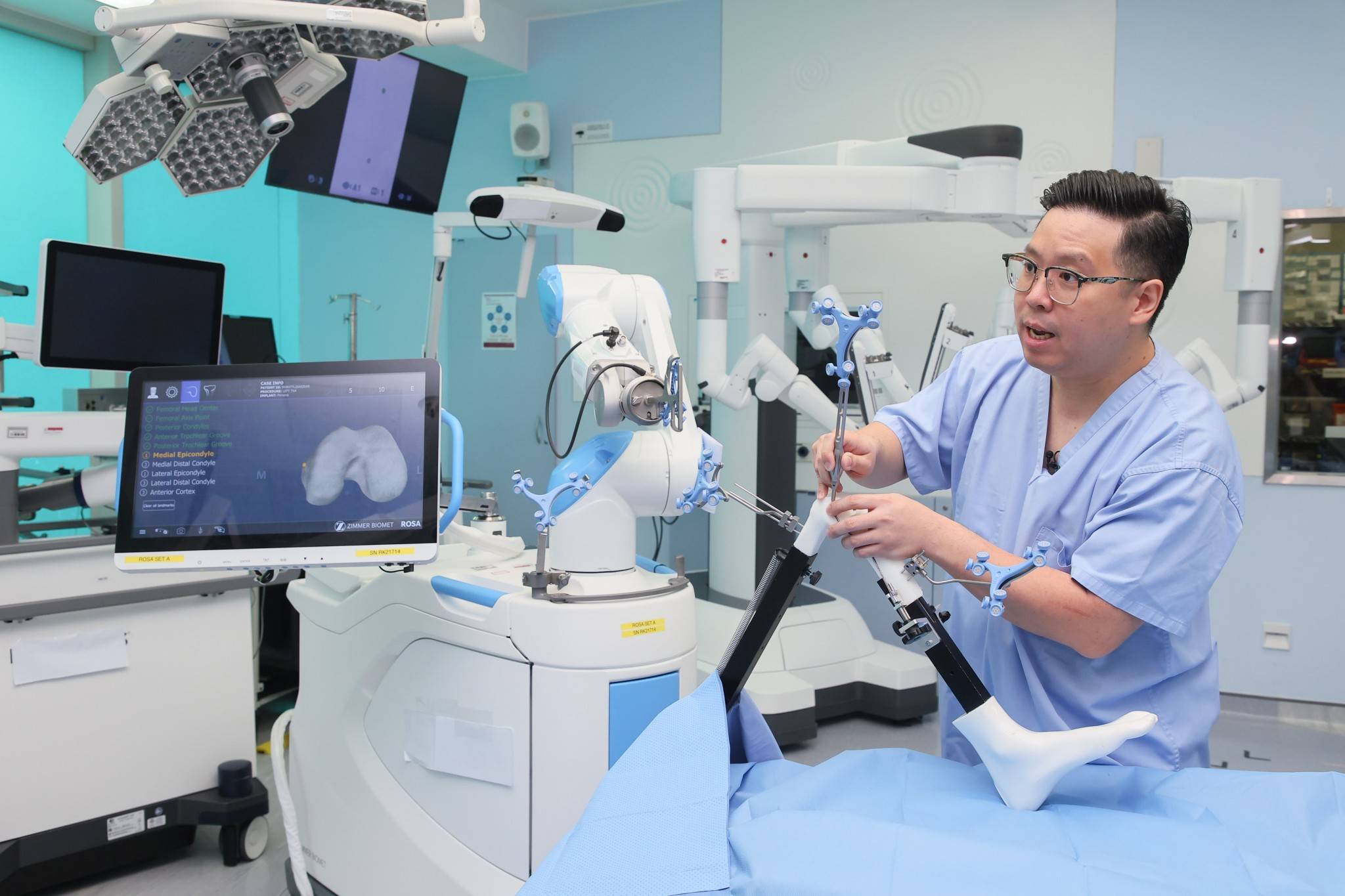

Maintaining Balance of Periarticular Soft Tissues and Ligaments
The application of the optical tracking system and robotic arm assistance technology is the key to maintaining the balance of the knee ligaments and soft tissues. The optical tracking system can real-time monitor the position of the patient's knee joint and the structure of the bone, and transmit the data to the computer. Doctors can then precisely plan the surgery based on these data to avoid unnecessary damage to the soft tissues. The robot will collect and digitize the data about the knee joint, followed by quantitative data analysis of ligament tension, allowing the doctor to make a more ideal intraoperative plan and reduce the damage to the ligament tissues.
Reduced Surgical Trauma and Pain
Compared to traditional joint replacement surgery, robot-assisted total knee replacement surgery is more minimally invasive, effectively reducing soft tissue injury, blood loss, and the risk of postoperative complications, thereby reducing postoperative pain.
Faster Recovery
With robot-assisted total knee replacement surgery, combined with the latest ‘Enhanced Recovery After Surgery [ERAS] ‘ rehabilitation concepts, patients can recover faster and regain their functional independence more quickly.

Improved Durability
With medical advancements, the materials and designs of artificial joints have been significantly improved. Currently, over 90% of artificial joints have a lifespan of 10 years or more, and approximately 80% of artificial joints have a lifespan of 20 years or more.

Robot-Assisted Total Knee Replacement Surgery vs. Traditional Joint Replacement Surgery
| Traditional Instrument Surgery | Robotic Surgery | |
| Positioning Method | Instruments | Optical |
| Preoperative 3D Digital Planning | X | ✓ |
| Ligament Tension Assessment | Surgeon dependent | Quantitative data analysis by robot |
| Cutting Assistance | Traditional Instruments | Robotic |
| Accuracy of bone cut and implant placement | Surgeon dependent | Accurate |
| Blood Loss | General | Less |
| Soft tissue Trauma | More | Less |
| Length of Stay | Longer | Shorter |
| Postoperative Pain | More | Less |
| Recovery Speed | General | Faster |
Am I suitable for robot-assisted total knee replacement?
Robot-assisted total knee replacement surgery is generally suitable for all patients who need to undergo total knee replacement surgery, but patient still needs to be evaluated and determined by an orthopedic specialist doctor to decide which surgical method is most suitable for him or her.
How long can I recover to normal after knee replacement?
With the progress of rehabilitation, patients can gradually return to normal work and life. For sedentary work, such as clerical office work, patients can usually resume normal work within 1-2 months after surgery. But if engaged in heavy manual labor work, such as construction, patients need 6 months to fully recover. Patient is recommended to consult and follow the doctor's instructions, and to carry out post-operative rehabilitation training to accelerate the recovery process.
Complications after knee replacement
With the advancement of technology, the risk of complications after knee replacement is much reduced. The related complications include infection, thrombosis, nerve damage, knee instability, persistent knee pain, joint stiffness etc. However, we can reduce the risk of complications after knee replacement through the following preventive measures:
- Perform pre-operative exercise and training as directed by the doctor
- Post-operative lower limb rehabilitation exercises
- Maintain good personal hygiene
- Take anti-thrombotic medications as instructed by the doctor for a period of time after surgery
- Weight control
- Quit smoking