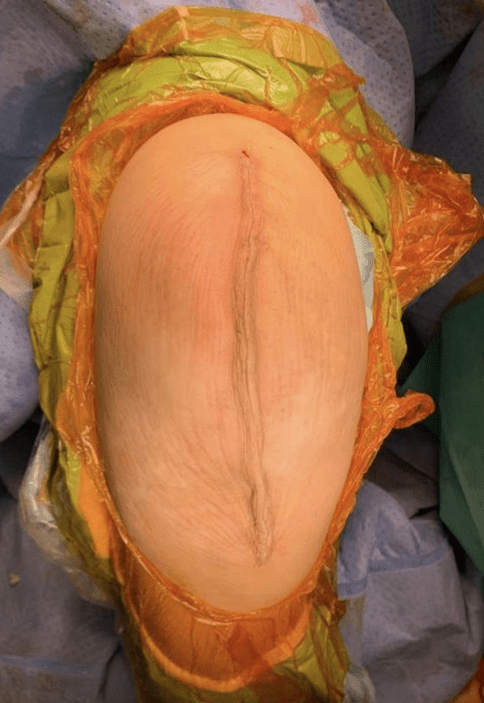
Elderly individuals may require knee replacement surgery due to knee joint degeneration. With advancements in medical technology, surgeries have become more personalized. In addition to using robotic arms to enhance surgical efficacy, there is now a greater emphasis on post-operative recovery and care. Among these advancements is the "non-invasive wound suturing technique," which helps patients recover their wounds more effectively.
Joint replacement surgery is a medium to large-scale operation, with wounds measuring about 14 to 16 centimeters. After surgery, sutures or staples are used to suture the wound until it heals. Suturing techniques have evolved over time, with the medical field now using self-dissolving sutures. While this method eliminates the need for suture removal, it still introduces foreign materials into the body, which may not yield the best healing results.
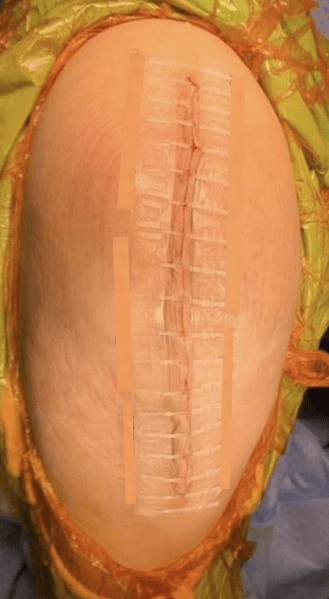
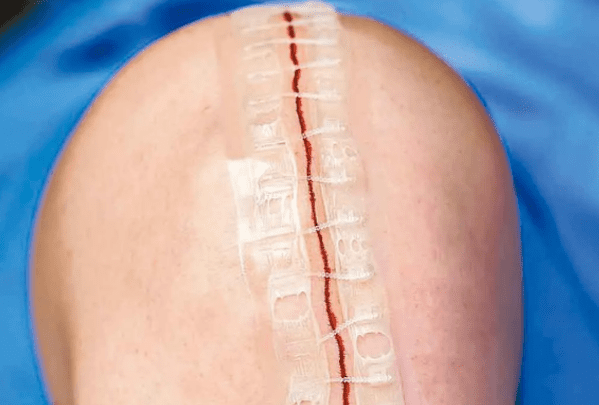
Two years ago, the "non-invasive wound suturing technique" was introduced in Hong Kong. The principle involves applying a material resembling a zipper directly onto the wound and then tightening it, eliminating the need for puncturing or inserting foreign objects into the body. This achieves a suturing effect, and the zipper can be removed about two weeks post-operation, with the "unzipping" process taking only a few seconds.
The term "zipper" might evoke concerns about securely protecting the wound. However, local experience has shown that over a hundred cases utilizing this technique have not resulted in wound dehiscence nor wound complication, with the improvement of less scarring. This is primarily because the technique provides better protection, reducing external stimuli and consequently lowering the risk of scarring. Additionally, this technique can be applied not only to knee replacement surgeries but also to any surgical procedure on the body.
In addition to improvements in suturing techniques, the dressings used to protect wounds have also evolved. The new generation of dressings combines different layers to achieve waterproof effects and incorporates silver ions, which can kill bacteria, thereby providing antimicrobial properties and preventing infections. When patients have their dressings removed, they can also take off the "zipper" simultaneously, saving time and creating an effective protective combination.